GraphQL
What is GraphQL?
/users, /posts, /comments), GraphQL typically exposes a single endpoint (usually /graphql). Clients send a query describing exactly the data structure they need, and the server returns a JSON response matching that structure.Core Concepts
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Code Example: The Schema
Comparisons: GraphQL vs. REST
| Feature | REST | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoints | Multiple (resource-based) | Single (usually /graphql) |
| Data Fetching | Fixed structure (Over/Under-fetching) | Client defines exact structure |
| Versioning | v1, v2 URL prefixes | Evolution via deprecation (schema-first) |
| Caching | Built-in HTTP caching | Requires specialized setup (e.g. Apollo) |
| Performance | Larger payloads, simple processing | Smaller payloads, complex server processing |
When to Use GraphQL?
1.
2.
3.
Debugging GraphQL in Apidog
1. Creating the Request
1.
2.
POST.3.

2. Intelligent Query Editing
Fetch Schema to download the type definitions from the server.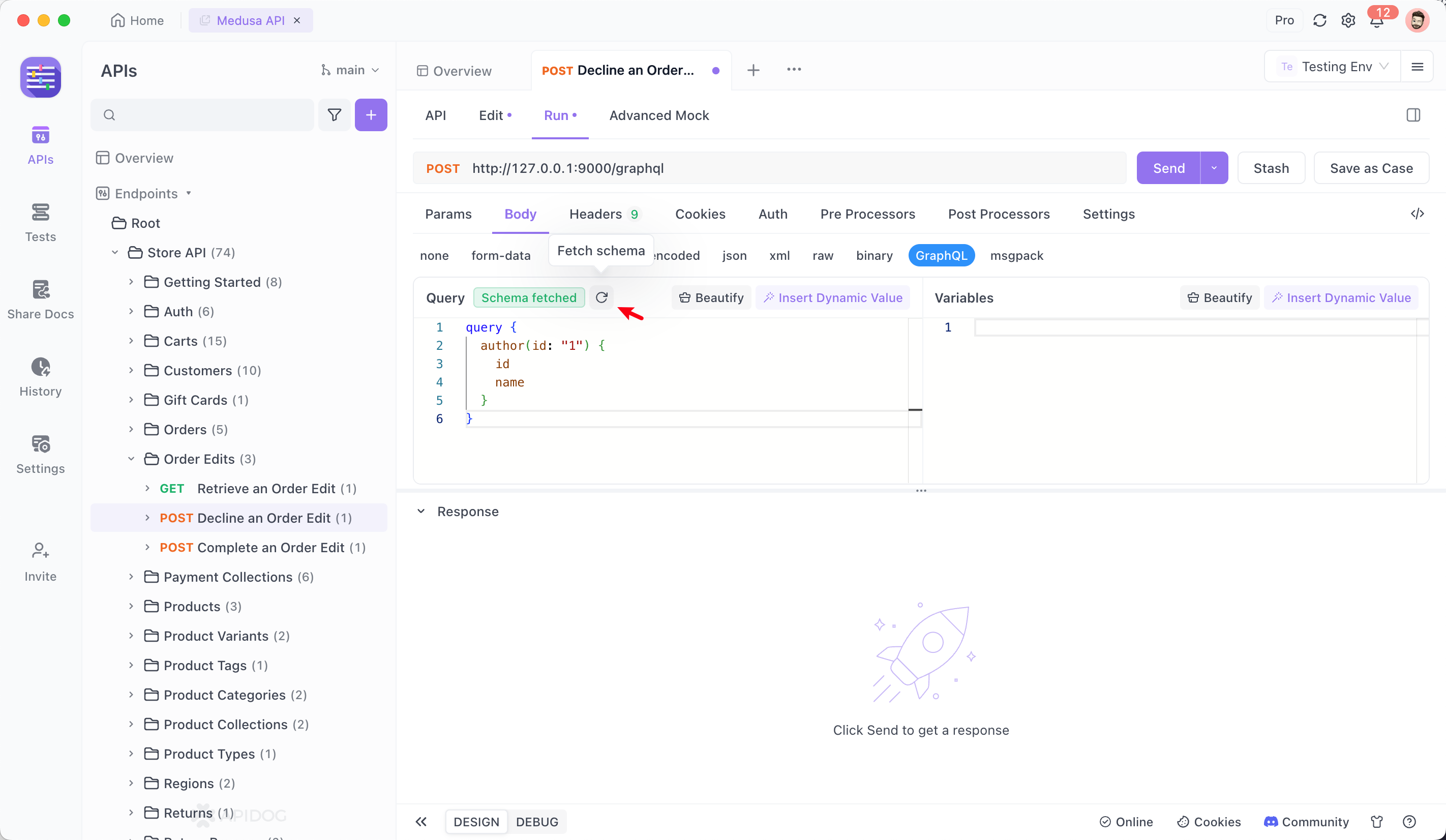
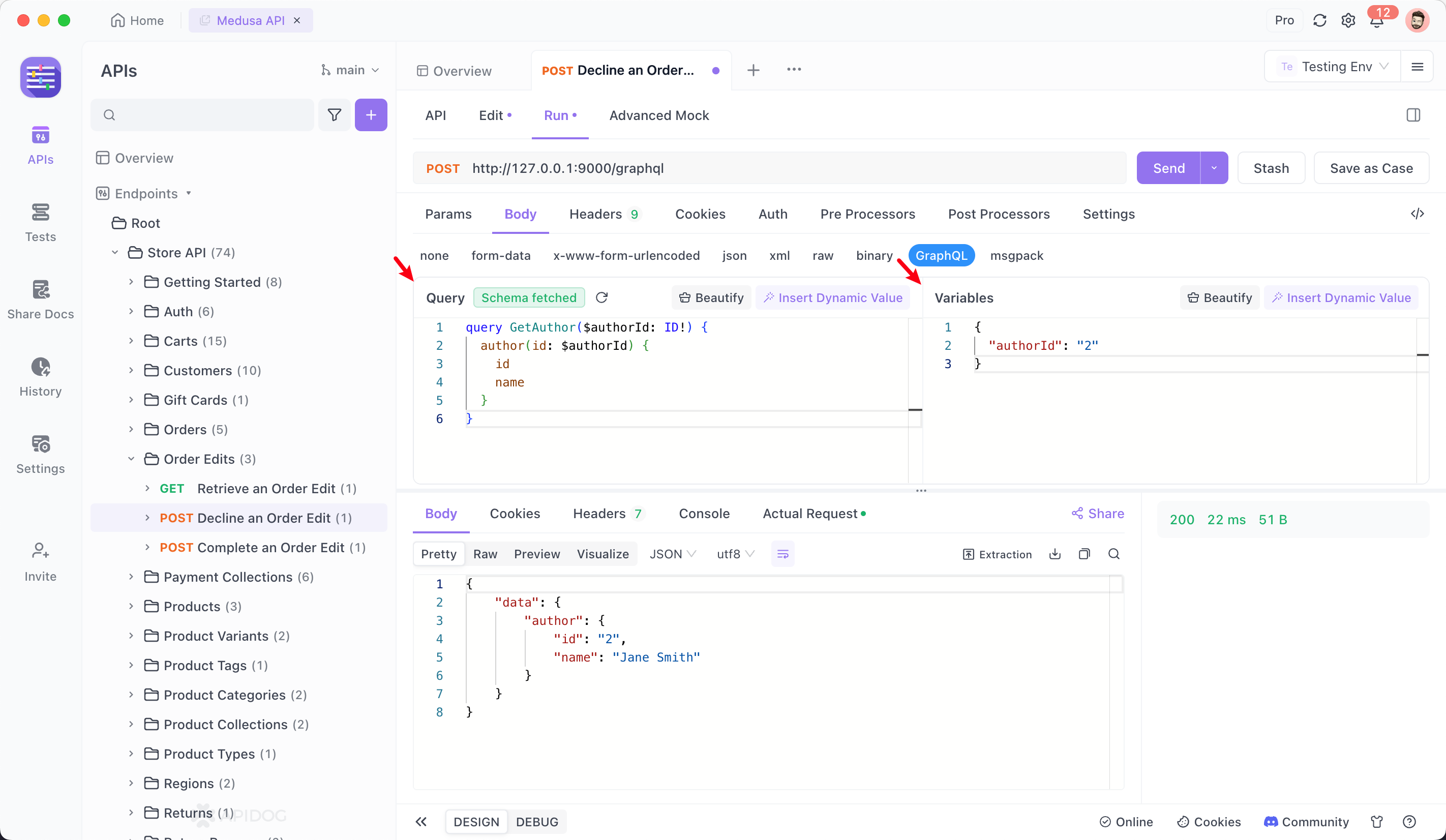
3. Using Variables
{
"id": "123"
}
Key Takeaways
/graphql) for all data interactions.Modified at 2026-02-12 06:23:15